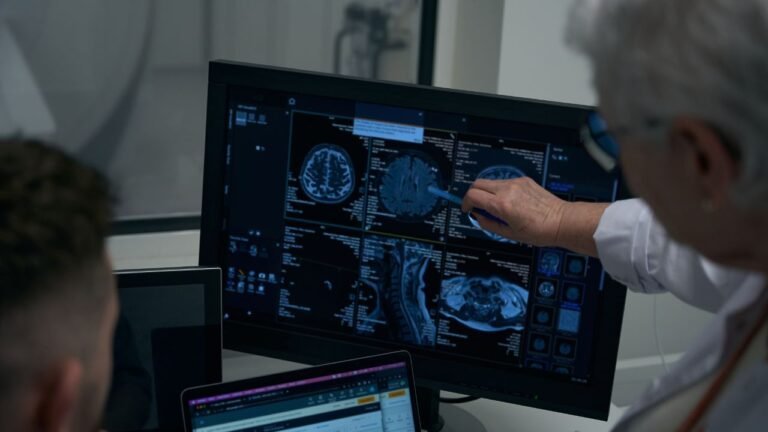
In today’s fast-paced world, neurological disorders have become increasingly common, and one such condition that affects millions of people worldwide is a brain tumor. A brain tumor refers to an abnormal growth of cells in the brain or the surrounding tissues. It can affect individuals of any age, from children to the elderly, and can have a significant impact on their overall health and well-being.
Causes of Brain Tumors
While the exact cause of brain tumors remains unknown, several risk factors have been identified. These include:
- Genetics: Certain genetic conditions, such as neurofibromatosis, Von Hippel-Lindau disease, and Li-Fraumeni syndrome, can increase the risk of developing brain tumors.
- Exposure to radiation: Previous exposure to ionizing radiation, such as radiation therapy for other cancers or radiation accidents, may increase the likelihood of developing a brain tumor.
- Age: Some types of brain tumors are more common in specific age groups. For example, medulloblastomas are more prevalent in children, while glioblastomas are more common in older adults.
- Environmental factors: Certain environmental factors, such as exposure to certain chemicals or toxins, may contribute to the development of brain tumors.
Symptoms of Brain Tumors
The symptoms of a brain tumor can vary depending on its size, location, and rate of growth. Some common symptoms include:
- Headaches: Persistent or worsening headaches, especially in the morning, can be a sign of a brain tumor.
- Seizures: Unexplained seizures, especially in individuals with no history of seizures, should be evaluated by a medical professional.
- Changes in vision or hearing: Blurred vision, double vision, or hearing problems can occur when a brain tumor affects the optic or auditory nerves.
- Balance and coordination difficulties: Brain tumors can affect motor skills, leading to problems with balance and coordination.
- Memory and cognitive issues: Cognitive impairments, memory loss, and difficulty concentrating can be indicative of a brain tumor.
Treatment Options
The treatment for a brain tumor depends on various factors, including the type, size, and location of the tumor, as well as the overall health of the patient. Some common treatment options include:
- Surgery: Surgical removal of the tumor is often the first line of treatment if the tumor is accessible and its removal will not cause significant damage to surrounding brain tissue.
- Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy X-rays or other forms of radiation to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells or inhibit their growth. It is often used in combination with other treatment modalities.
- Targeted therapy: Targeted therapy uses drugs that specifically target certain molecules or genetic mutations present in cancer cells, minimizing damage to healthy cells.
- Supportive care: Palliative care and supportive therapies aim to improve the quality of life for individuals with brain tumors by managing symptoms and providing emotional support.
Conclusion
Brain tumors can have a profound impact on individuals and their families. Early detection, prompt medical intervention, and access to appropriate treatment options are crucial in managing brain tumors effectively. If you or a loved one experience any persistent or concerning symptoms, it is essential to seek medical advice to ensure timely diagnosis and appropriate care.
Anand Neuro Care, under the expertise of Dr. Anand Kumar Jha, is committed to providing comprehensive brain and spine care. With a focus on patient-centric treatment and the latest advancements in neurosurgery, Anand Neuro Care strives to improve the lives of individuals affected by brain tumors and other neurological conditions.